Blog Medical Harbour
Articles focused on letting you know the latest news surrounding new technologies allied to productivity and quality of life - SubscribeGeneral Anatomy – Athena Hub Workspaces
The word "anatomy" comes from the Greek, meaning to cut parts. In other words, it studies the shape and structure of the human body, isolating each part.
The most used technique in courses of medicine, dentistry or others in the health area is dissection, which uses cuts for better visualization of all parts of the body.
Endocrine System – Athena Hub Workspaces
The endocrine system is responsible for producing our hormones. It consists of a set of glands released into the blood, which travel throughout our body, until reaching the organs where they act.
The endocrine system coordinates all the functions of our body along with the nervous system. And who makes the integration of these two systems is the hypothalamus, a group of renowned nerve cells at the base of the brain.
Facial Muscles – Athena Hub Workspaces
The facial muscles are located under the skin of the face and most of them originate from the skull or fibrous structures and radiate to the skin through an elastic tendon.
Digestive System – Athena Hub Workspaces
The digestive system is formed by the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and anus. The following accessory glands are also part of this system: salivary glands, pancreas and liver.
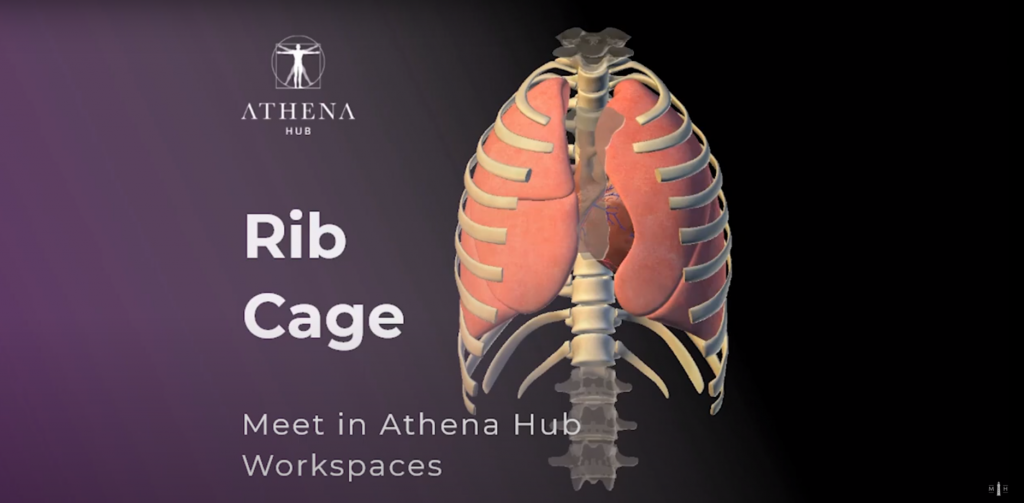
Rib Cage – Athena Hub Workspaces
The rib cage, formed by the sternum, ribs and spine, protects the lungs and other organs in the chest.
Mouth and Teeth – Athena Hub Workspaces
The mouth is part of the digestive system being the first place through which the food passes, in addition the mouth has a whole system of teeth which has the function of chewing and grinding the meals so that the rest of the process is done well.
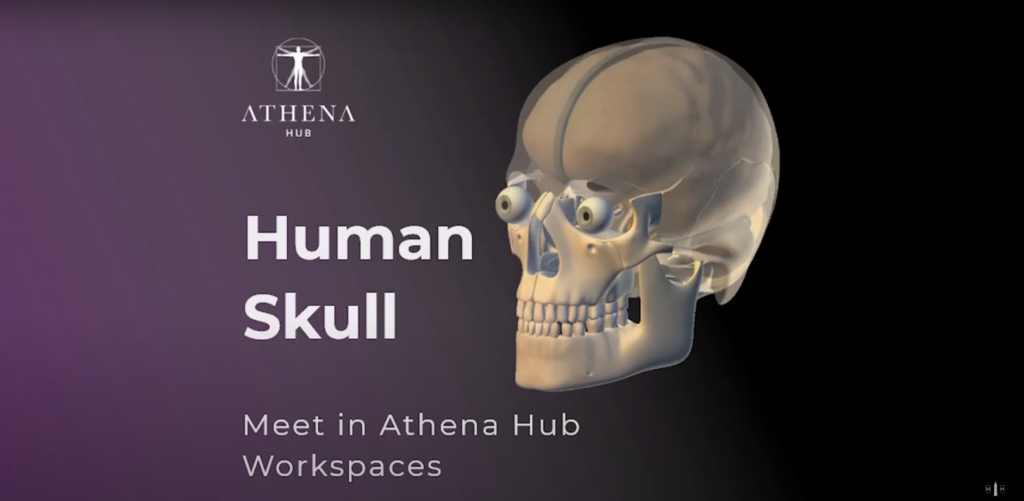
Skull protects Brain – Athena Hub Workspaces
The human skull has the function of protecting the brain. It can be divided into two parts: the neurocranium, which forms a protective box for the brain, and the facial or splanchnocranium skeleton. The neurocranium corresponds to the upper and posterior part of the skull that supports the structures of the face and protects the brain.
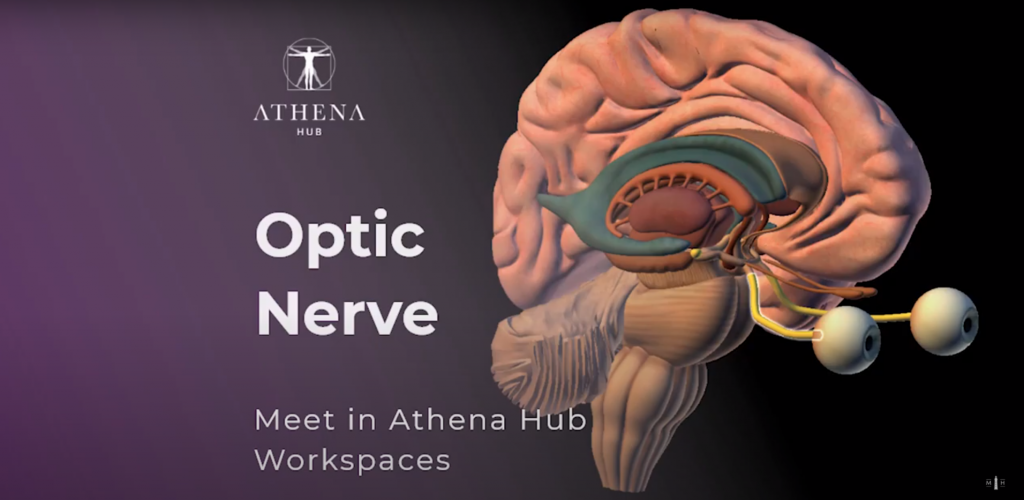
Optic Nerve – Athena Hub Workspaces
The Optic Nerve is the second cranial nerve wich, along with the Olfactory Nerve, is an extension of the Central Nervous System.
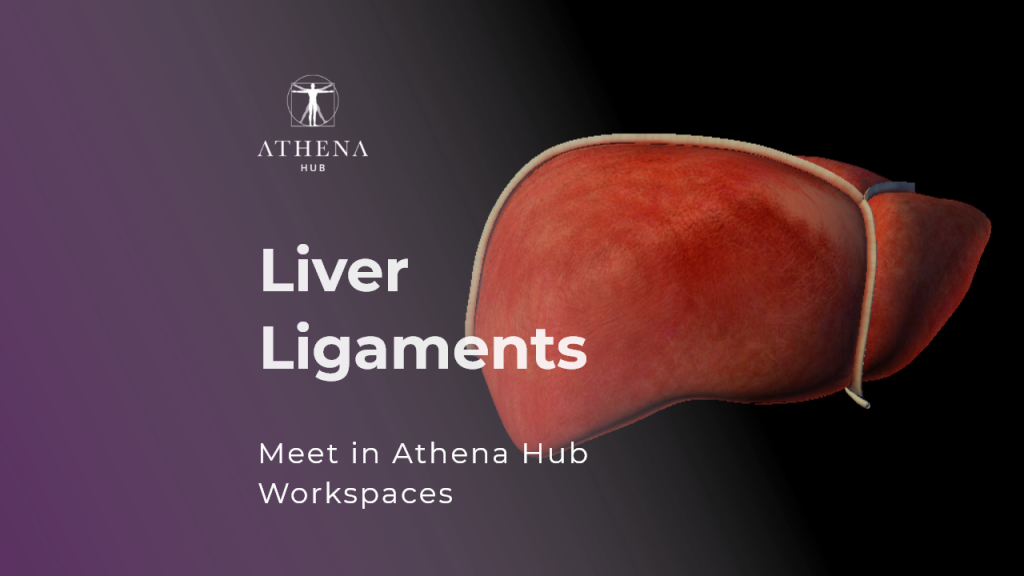
Ligaments of the Liver – Athena Hub Workspaces
There are five ligaments that are directly related to the liver and trey’are called: Coronary Ligament, Left Triangular Ligament, Sickle Ligament, Liver Round Ligament, and Venous Ligament.
Arterial System X Venous System – Athena Hub Workspaces
Did you know that venous blood, rich in carbon dioxide, is pumped from the heart to the lungs through the pulmonary arteries? While arterial blood, rich in oxygen gas, is pumped from the heart to body tissues through the aorta artery.